Scheduling guide
SQLMesh currently offers two ways of scheduling model evaluation:
- Using the built-in scheduler
- By integrating with Airflow
Built-in scheduler
SQLMesh includes a built-in scheduler that schedules model evaluation without any additional tools or dependencies. It provides all the functionality needed to use SQLMesh in production.
By default, the scheduler stores your SQLMesh project's state (information about models, data, and run history) in the SQL engine used to execute your models. Some engines, such as BigQuery, are not optimized for the transactions the scheduler executes to store state, which may degrade the scheduler's performance.
When running the scheduler in production, we recommend evaluating its performance with your SQL engine. If you observe degraded performance, consider providing the scheduler its own transactional database such as PostgreSQL to improve performance. See the connections guide for more information on providing a separate database/engine for the scheduler.
To perform model evaluation using the built-in scheduler, run the following command:
The command above will automatically detect missing intervals for all models in the current project and then evaluate them:
$ sqlmesh run
All model batches have been executed successfully
sqlmesh_example.example_incremental_model ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 100.0% • 1/1 • 0:00:00
sqlmesh_example.example_full_model ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 100.0% • 1/1 • 0:00:00
Note: The sqlmesh run command performs model evaluation based on the missing data intervals identified at the time of running. It does not run continuously, and will exit once evaluation is complete. You must run this command periodically with a cron job, a CI/CD tool like Jenkins, or in a similar fashion.
Integrating with Airflow
Configuring the Airflow cluster
SQLMesh natively integrates with the popular open source workflow orchestrator Apache Airflow, both self-hosted and managed (e.g. Google Cloud Composer, Amazon MWAA, Astronomer).
To integrate with Airflow, ensure that you meet the prerequisites, then perform the following:
-
Install the SQLMesh Python package on all nodes of the Airflow cluster using the following command:
pip install sqlmeshNote: The Airflow webserver must be restarted after installation.
-
Within the Airflow
dags/folder, create a file calledsqlmesh.py. -
Within that file add the following, making sure to replace "spark" with your engine and
spark_catalogwith your default catalog:from sqlmesh.schedulers.airflow.integration import SQLMeshAirflow sqlmesh_airflow = SQLMeshAirflow("spark", default_catalog="spark_catalog") for dag in sqlmesh_airflow.dags: globals()[dag.dag_id] = dagThe example above uses
sparkas the engine of choice. Other engines can be configured instead by providing a corresponding string as an argument to theSQLMeshAirflowconstructor. Supported strings are"spark","databricks","snowflake","bigquery","redshift"and"trino". See the Airflow Cluster Configuration for full list of arguments and their descriptions.
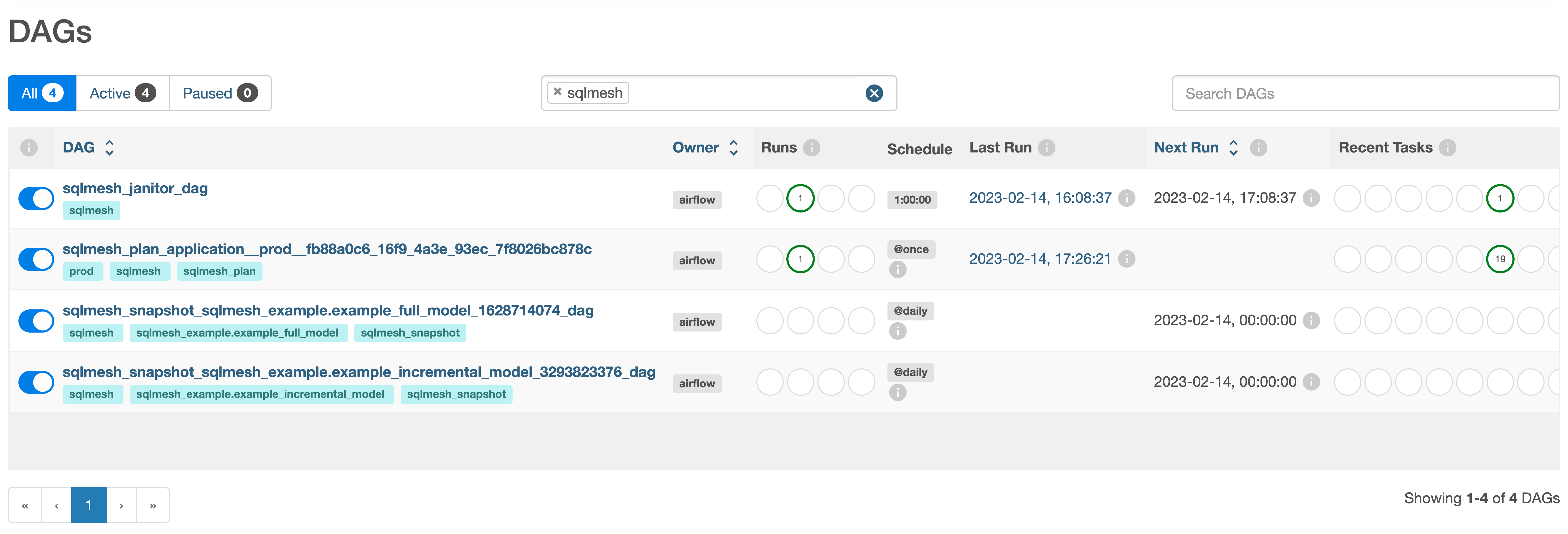
After setup is completed, the sqlmesh_janitor_dag DAG should become available in the Airflow UI when filtered by the sqlmesh tag:
Configuring the client
On the client side, you must configure the connection to your Airflow cluster in the config.yaml file as follows:
default_scheduler:
type: airflow
airflow_url: http://localhost:8080/
username: airflow
password: airflow
Alternatively, the configuration above can be generated automatically as part of the project initialization using the airflow template:
For Airflow configuration types specific to Google Cloud Composer, configure the file as follows:
default_scheduler:
type: cloud_composer
airflow_url: https:/XXXXXXXX.composer.googleusercontent.com/
Note: Guidelines for integrating with managed offerings other than Google Cloud Composer will be added later.
Running the plan command
Run the sqlmesh plan command to apply all changes on the target Airflow cluster.
Below is example output from running the sqlmesh plan command in the example project generated by the sqlmesh init command:
$ sqlmesh plan
======================================================================
Successfully Ran 1 tests against duckdb
----------------------------------------------------------------------
Summary of differences against `prod`:
└── Added Models:
├── sqlmesh_example.example_incremental_model
└── sqlmesh_example.example_full_model
Models needing backfill (missing dates):
├── sqlmesh_example.example_incremental_model: (2020-01-01, 2023-02-13)
└── sqlmesh_example.example_full_model: (2023-02-13, 2023-02-13)
Enter the backfill start date (eg. '1 year', '2020-01-01') or blank for the beginning of history: 2023-02-13
Apply - Backfill Tables [y/n]: y
Waiting for the plan application DAG 'sqlmesh_plan_application__prod__fb88a0c6_16f9_4a3e_93ec_7f8026bc878c' to be provisioned on Airflow
Track plan application progress using link
Once the command runs, the following DAGs will become available within the Airflow UI: