GitHub Actions CI/CD Bot
The GitHub Actions CI/CD Bot enables teams to automate their SQLMesh projects using GitHub Actions. It can be configured to perform the following things:
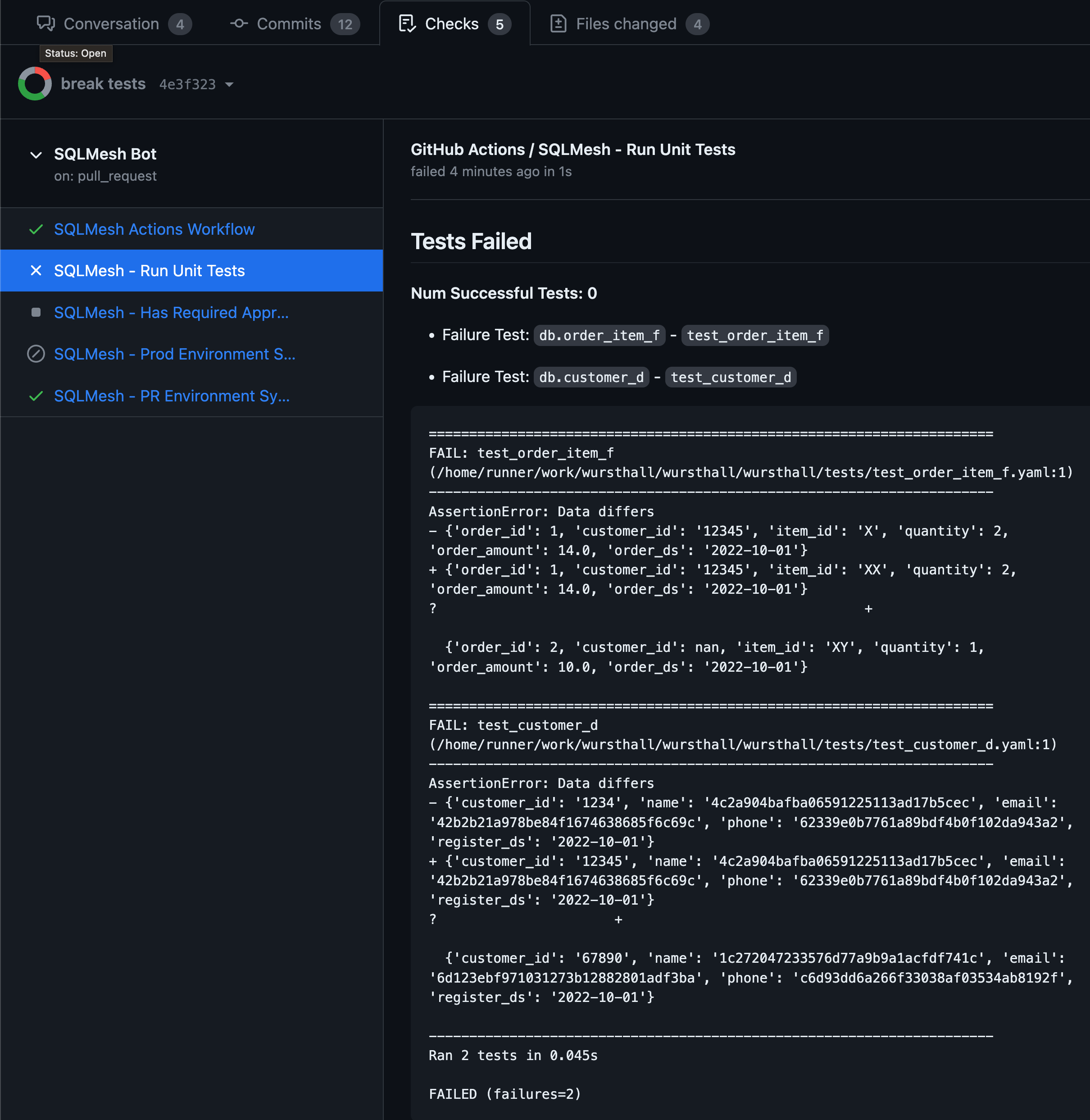
- Automatically run unit tests on PRs
- Automatically create PR environments that represent the code changes in the PR
- Automatically categorize and backfill data for models that have changed
- Automatically deploy changes to production with automatic data gap prevention and merge the PR
All of these features provide summaries and links to the relevant information in the PR so that you can easily see what is happening and why.
Due to the variety of ways that this bot can be configured, it is recommended to perform the initial setup and then explore the different configuration options to see which ones fit your use case.
Initial Setup
- Make sure SQLMesh is added to your project's dependencies and it includes the github extra (
pip install sqlmesh[github]). - Create a new file in
.github/workflows/sqlmesh.ymlwith the following contents:name: SQLMesh Bot run-name: 🚀SQLMesh Bot 🚀 on: pull_request: types: - synchronize - opened # The latest commit is the one that will be used to create the PR environment and deploy to production concurrency: group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.ref_name }} cancel-in-progress: true jobs: sqlmesh: name: SQLMesh Actions Workflow runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: # Required to access code in PR contents: write # Required to post comments issues: write # Required to update check runs checks: write # Required to merge pull-requests: write steps: - name: Setup Python uses: actions/setup-python@v4 - name: Checkout PR branch uses: actions/checkout@v4 with: ref: refs/pull/${{ github.event.issue.pull_request && github.event.issue.number || github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge - name: Install SQLMesh + Dependencies run: pip install -r requirements.txt shell: bash - name: Run CI/CD Bot run: | sqlmesh_cicd -p ${{ github.workspace }} github --token ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} run-all
Next checkout the Core Bot Behavior Configuration Guide to see how to configure the bot's core behavior. Then checkout Bot Configuration to see how to configure the bot's behavior in general. Finally, checkout Custom Workflow Configuration to see the full set of customizations available to the bot.
Core Bot Behavior Configuration Guide
There are two fundamental ways the bot can be configured: synchronized or desynchronized production code and data.
Synchronized vs. Desynchronized Deployments
Typically, CI/CD workflows for data projects follow a flow where code is merged into a main branch and then the production datasets that are represented by the code in main are eventually updated to match the code.
This could either be on merge, and therefore they will be updated after the refresh job completes, or it could be on a schedule where the refresh job is run on a schedule.
Either way the data in production is lagging behind the code in main and therefore code and data are desynchronized.
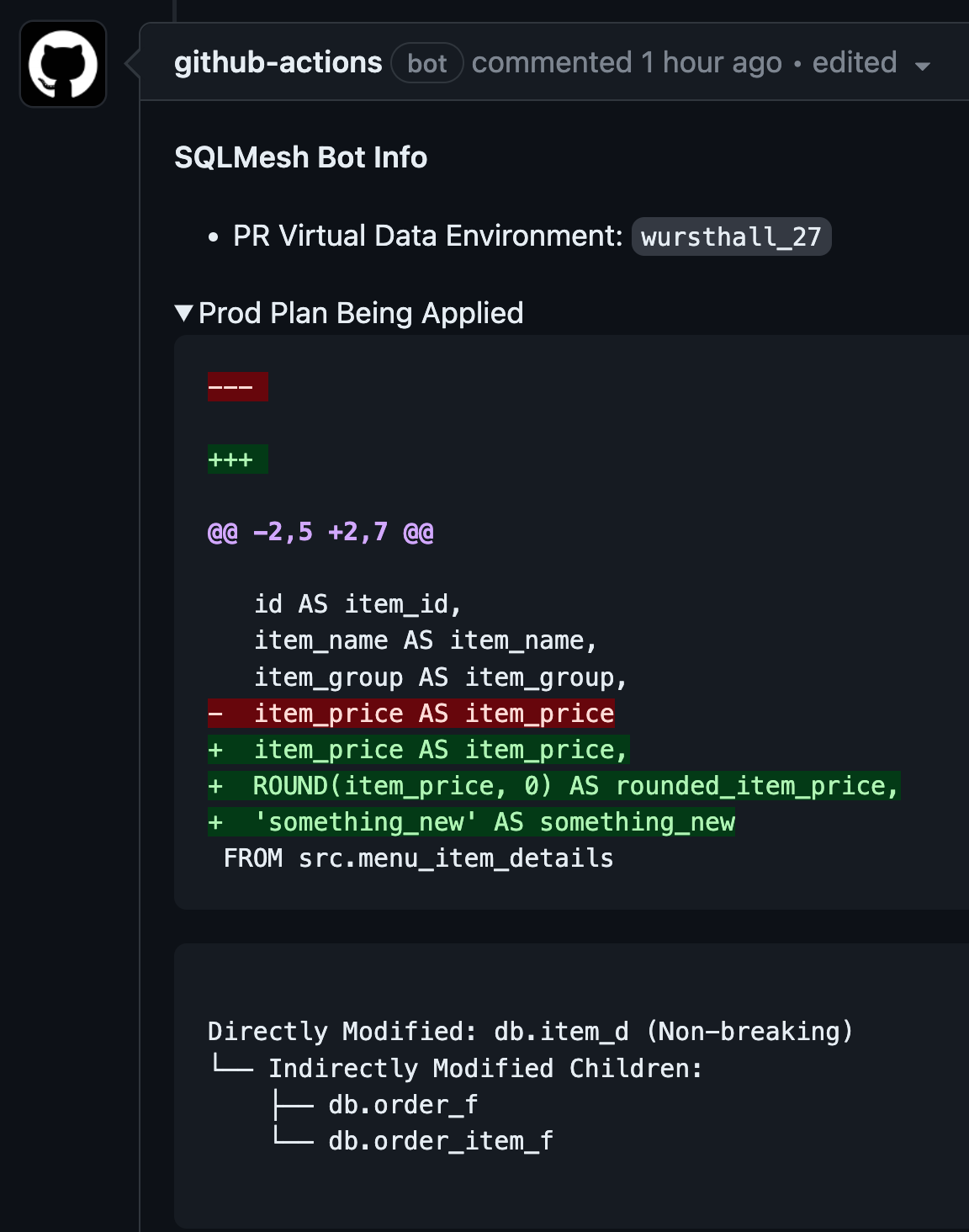
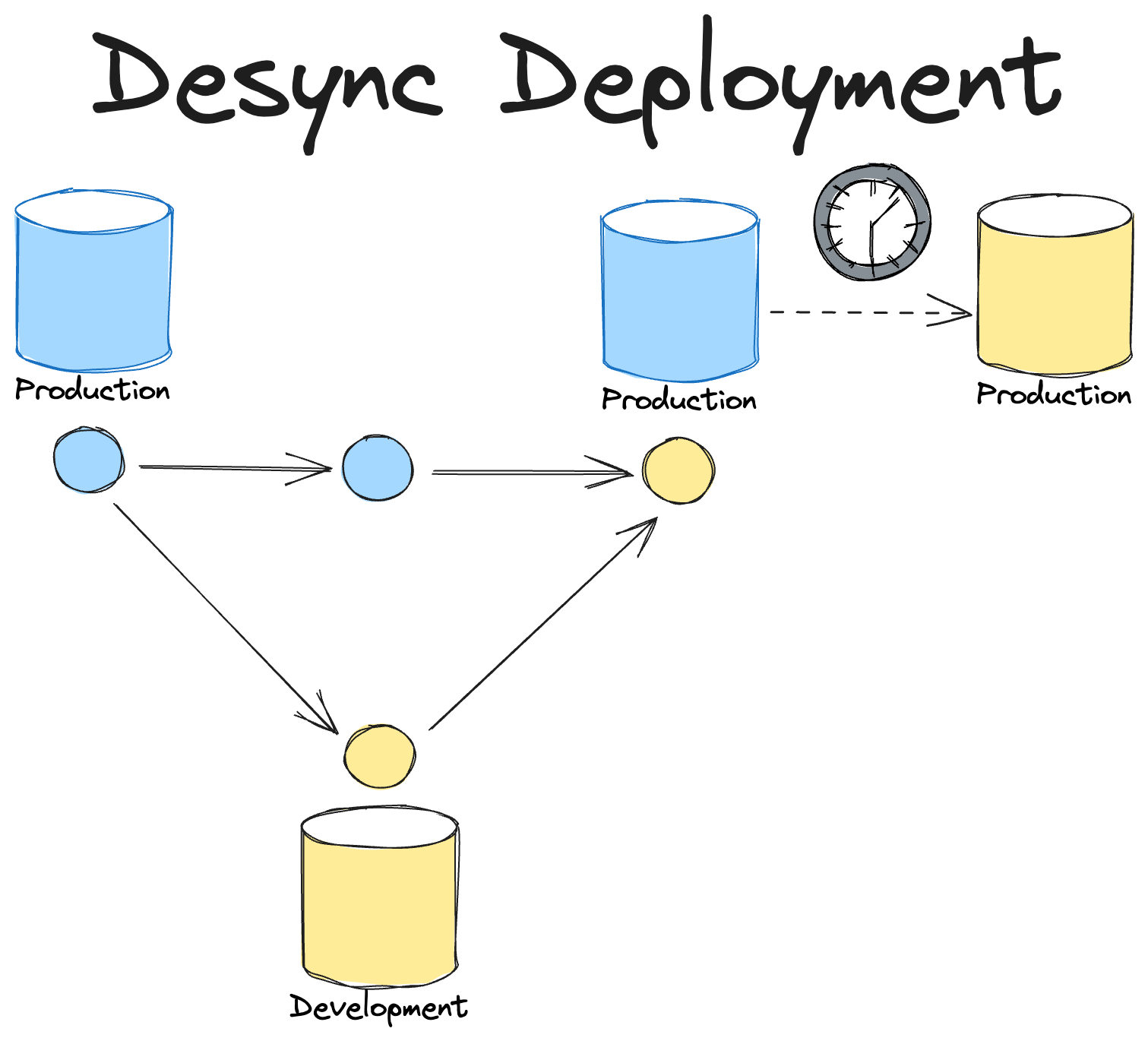 The advantage though of this approach is that users just need to merge a branch in order to see their changes eventually represented in production.
The disadvantage is that it can be difficult for users to know the current state of production is and when their changes will be live.
In addition, if an error occurs while the data in production is being updated then the data in production may never reflect the state that is represented in the main branch.
The advantage though of this approach is that users just need to merge a branch in order to see their changes eventually represented in production.
The disadvantage is that it can be difficult for users to know the current state of production is and when their changes will be live.
In addition, if an error occurs while the data in production is being updated then the data in production may never reflect the state that is represented in the main branch.
SQLMesh's virtual data environments offer a different approach where the deployment can be synchronized.
This means that dev datasets can be quickly deployed to production using SQLMesh's virtual update and then immediately after the branch is automatically merged to main.
Now the code and data in production are synchronized and users can see their changes immediately.
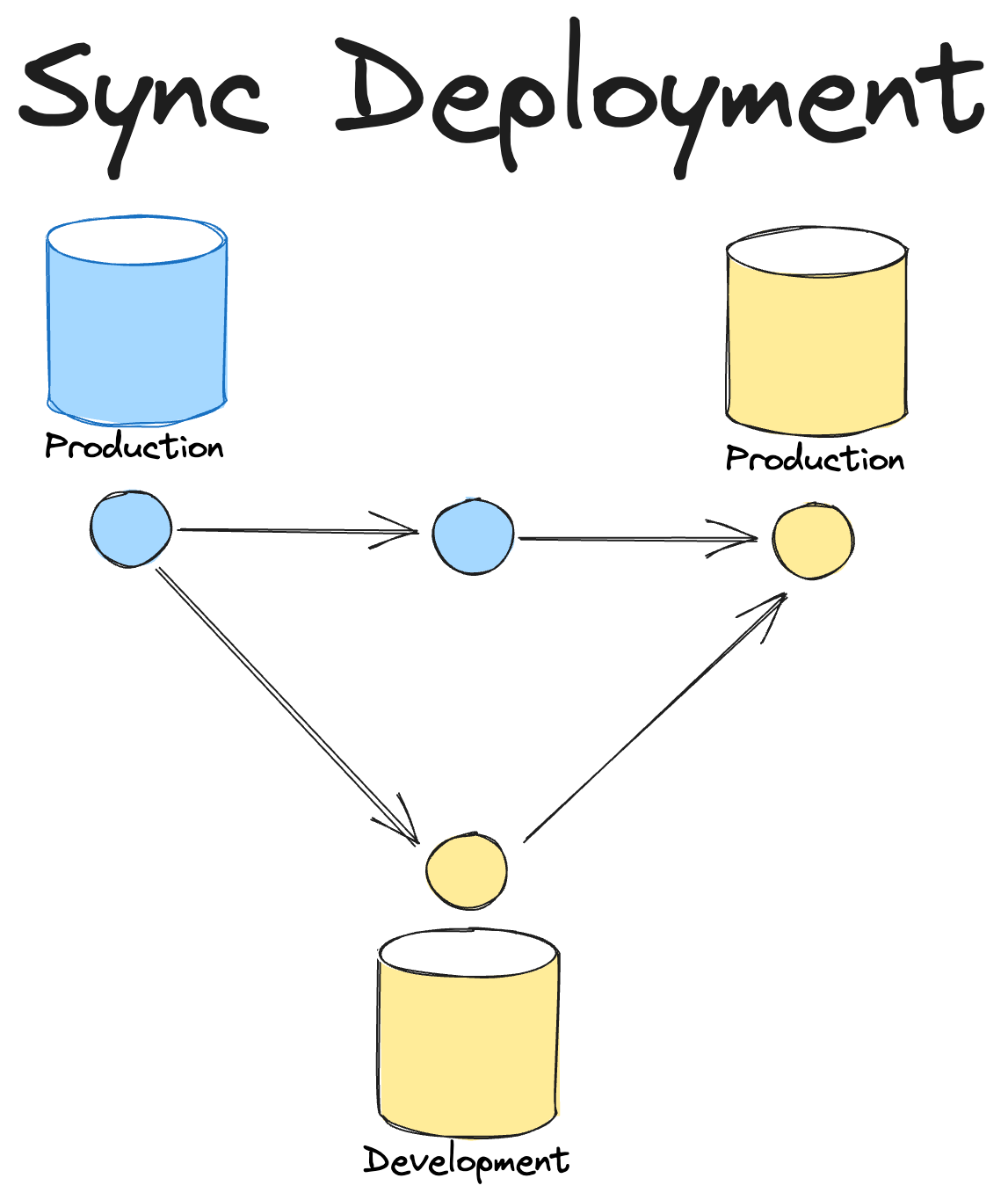 The disadvantage of this approach is that users can't simply merge a branch to get their changes into production since SQLMesh needs to be able to deploy the changes and then perform the merge itself.
As a result it requires a "signal" from users to indicate that they want a change deployed to production that will then trigger the bot to deploy the changes and then merge the PR.
The disadvantage of this approach is that users can't simply merge a branch to get their changes into production since SQLMesh needs to be able to deploy the changes and then perform the merge itself.
As a result it requires a "signal" from users to indicate that they want a change deployed to production that will then trigger the bot to deploy the changes and then merge the PR.
SQLMesh's GitHub CI/CD Bot supports either approach and it is up to each team which mode is the best fit given their organization's constraints.
Synchronized Production Code and Data Configuration
Regardless of signal approach being used, the bot needs to be configured to use the merge method you want to use when merging the PR after deploying to production.
In this example we configured the merge method to be squash. See Bot Configuration for more details on the merge_method option.
Required Approval Signal
One way to signal to SQLMesh that a PR is ready to go to production is through the use of "Required Approvers". In this approach users configure their SQLMesh project to list users that are designated as "Required Approver" and then when the bot detects an approval was received from one of these individuals then it determines that it is time to deploy to production. This pattern can be a great fit for teams that already have an approval process like this in place and therefore it actually removes an extra step from either the author or the approver since SQLMesh will automate the deployment and merge until of it having to be manually done.
Required Approval Configuration
In order to configure this pattern, you need to define a user in your SQLMesh project that has the "Required Approver" role.
The GitHub Actions workflow needs to be updated to trigger the action based on if a pull request review has come in.
Now if the bot detects an approval from this user then it will deploy the changes to production and merge the PR.
Deploy Command Signal
In this approach users can issue a /deploy command to the bot to signal that they want the changes in the PR to be deployed to production.
This pattern is more flexible than the required approval pattern.
Deploy command signal can be used alongside the required approval signal or on its own.
The deploy command, if issued, overrides the required approval signal and will deploy the changes to production and merge the PR.
Deploy Command Configuration
This command must be enabled in the bot's configuration.
Optionally, a command_namespace can be configured to avoid clashing with other bots. See Bot Configuration for more details on the command_namespace option.
The GitHub Actions workflow needs to be updated to trigger the action based on if a comment has been created.
Note: the issue_comment event will not work until this change is merged into your main branch. Therefore, to enable this you will need to make the change in a branch, merge, and then future branches will support the deploy command.
Desynchronized Production Code and Data Configuration
In order to support this pattern we need to add an additional step to the workflow that will run the deploy-production command after the merge to main.
In addition we need to also update some prior steps with if checks to differentiate the merge vs. non-merge behavior.
Make sure that "Required Approvers" are not configured (they are not by default) and "Deploy Command" is not enabled (it is not by default).
Bot Configuration
The bot's behavior is configured using your project's config.yaml or config.py file. See SQLMesh Configuration for more details on how to generally setup and configure SQLMesh.
Below is an example of how to define the default config for the bot in either YAML or Python.
Configuration Properties
| Option | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
invalidate_environment_after_deploy |
Indicates if the PR environment created should be automatically invalidated after changes are deployed. Invalidated environments are cleaned up automatically by the Janitor. Default: True |
bool | N |
merge_method |
The merge method to use when automatically merging a PR after deploying to prod. Defaults to None meaning automatic merge is not done. Options: merge, squash, rebase |
string | N |
enable_deploy_command |
Indicates if the /deploy command should be enabled in order to allowed synchronized deploys to production. Default: False |
bool | N |
command_namespace |
The namespace to use for SQLMesh commands. For example if you provide #SQLMesh as a value then commands will be expected in the format of #SQLMesh/<command>. Default: None meaning no namespace is used. |
string | N |
auto_categorize_changes |
Auto categorization behavior to use for the bot. If not provided then the project-wide categorization behavior is used. See Auto-categorize model changes for details. | dict | N |
default_pr_start |
Default start when creating PR environment plans. If running in a mode where the bot automatically backfills models (based on auto_categorize_changes behavior) then this can be used to limit the amount of data backfilled. Defaults to None meaning the start date is set to the earliest model's start or to 1 day ago if data previews need to be computed. |
str | N |
skip_pr_backfill |
Indicates if the bot should skip backfilling models in the PR environment. Default: True |
bool | N |
pr_include_unmodified |
Indicates whether to include unmodified models in the PR environment. Default to the project's config value (which defaults to False) |
bool | N |
run_on_deploy_to_prod |
Indicates whether to run latest intervals when deploying to prod. If set to false, the deployment will backfill only the changed models up to the existing latest interval in production, ignoring any missing intervals beyond this point. Default: True |
bool | N |
Example with all properties defined:
Bot Output
Step outputs are created by the bot that capture the status of each of the checks that reach a conclusion in a run. These can be used to potentially trigger follow up steps in the workflow. These are the possible outputs (based on how the bot is configured) that are created by the bot:
run_unit_testshas_required_approvalpr_environment_syncedprod_plan_previewprod_environment_synced
There are many possible conclusions so the best use case for this is likely to check for success conclusion in order to potentially run follow up steps.
Note that in error cases conclusions may not be set and therefore you will get an empty string.
Example of running a step after pr environment has been synced:
In addition, there are custom outputs listed below:
created_pr_environment- set to"true"(a string with a value oftrue) if a PR environment was created for the first time. It is absent, or considered empty string if you check for it, if it is not created for the first timepr_environment_name- the name of the PR environment. It is output whenever PR environment synced check reaches a conclusion. Therefore make sure to check the status ofcreated_pr_environmentorpr_environment_syncedbefore acting on this output
Custom Workflow Configuration
You can configure each individual action to run as a separate step. This can allow for more complex workflows or integrating specific steps with other actions you want to trigger. Run sqlmesh_cicd github to see a list of commands that can be supplied and their potential options.
Github Action CI/CD Bot
Options:
-t, --token TEXT The Github Token to be used. Pass in `${{
secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}` if you want to use the one
created by Github actions
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
check-required-approvers Checks if a required approver has provided...
deploy-production Deploys the production environment
run-all Runs all the commands in the correct order.
run-tests Runs the unit tests
update-pr-environment Creates or updates the PR environments
Example Full Workflow
This workflow involves configuring a SQLMesh connection to Databricks and configuring access to GCP to talk to Cloud Composer (Airflow)
name: SQLMesh Bot
run-name: 🚀SQLMesh Bot 🚀
on:
pull_request:
types:
- synchronize
- opened
# Required if using required approvers to automate deployments
pull_request_review:
types:
- edited
- submitted
- dismissed
# Required if using comments to issue commands to the bot
issue_comment:
types:
- created
# The latest commit is the one that will be used to create the PR environment and deploy to production
concurrency:
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.ref_name }}
cancel-in-progress: true
jobs:
sqlmesh:
name: SQLMesh Actions Workflow
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: write
# Required to post comments
issues: write
# Required to update check runs
checks: write
# Required to merge
pull-requests: write
env:
SQLMESH__GATEWAYS__DATABRICKS__CONNECTION__TYPE: "databricks"
SQLMESH__GATEWAYS__DATABRICKS__CONNECTION__SERVER_HOSTNAME: "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
SQLMESH__GATEWAYS__DATABRICKS__CONNECTION__HTTP_PATH: "XXXXXXXXXXXX"
SQLMESH__GATEWAYS__DATABRICKS__CONNECTION__ACCESS_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.DATABRICKS_TOKEN }}
SQLMESH__DEFAULT_GATEWAY: "databricks"
steps:
- name: Setup Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: '3.9'
- name: Checkout PR branch
uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
ref: refs/pull/${{ github.event.issue.pull_request && github.event.issue.number || github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge
- name: Install Dependencies
run: pip install -r requirements.txt
shell: bash
- id: auth
name: Authenticate to Google Cloud
uses: google-github-actions/auth@v1
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GOOGLE_CREDENTIALS }}'
- name: Run CI/CD Bot
run: |
sqlmesh_cicd -p ${{ github.workspace }} github --token ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }} run-all
Example Screenshots
Automated Unit Tests with Error Summary
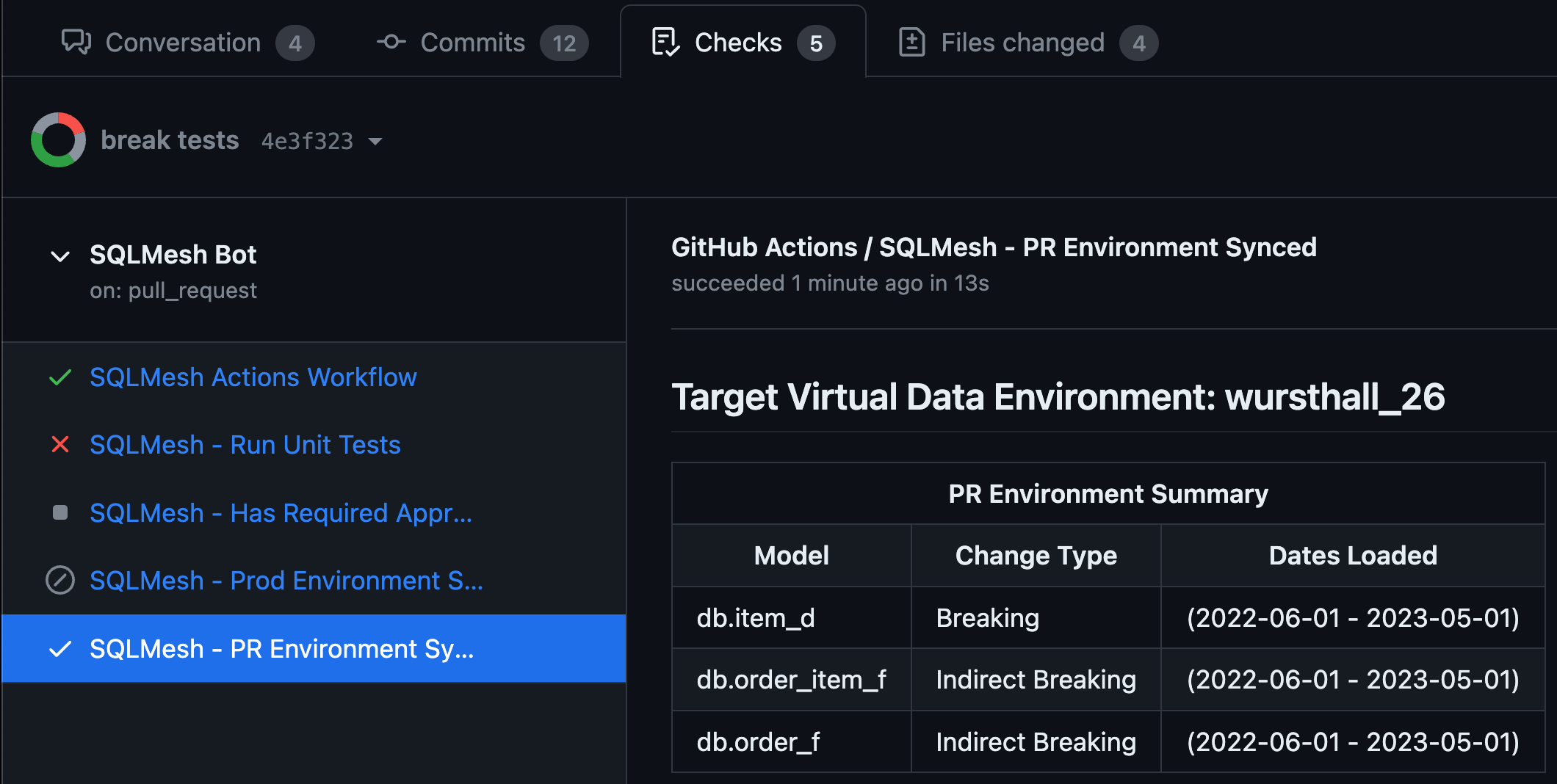
Automatically create PR Environments that represent the code changes in the PR
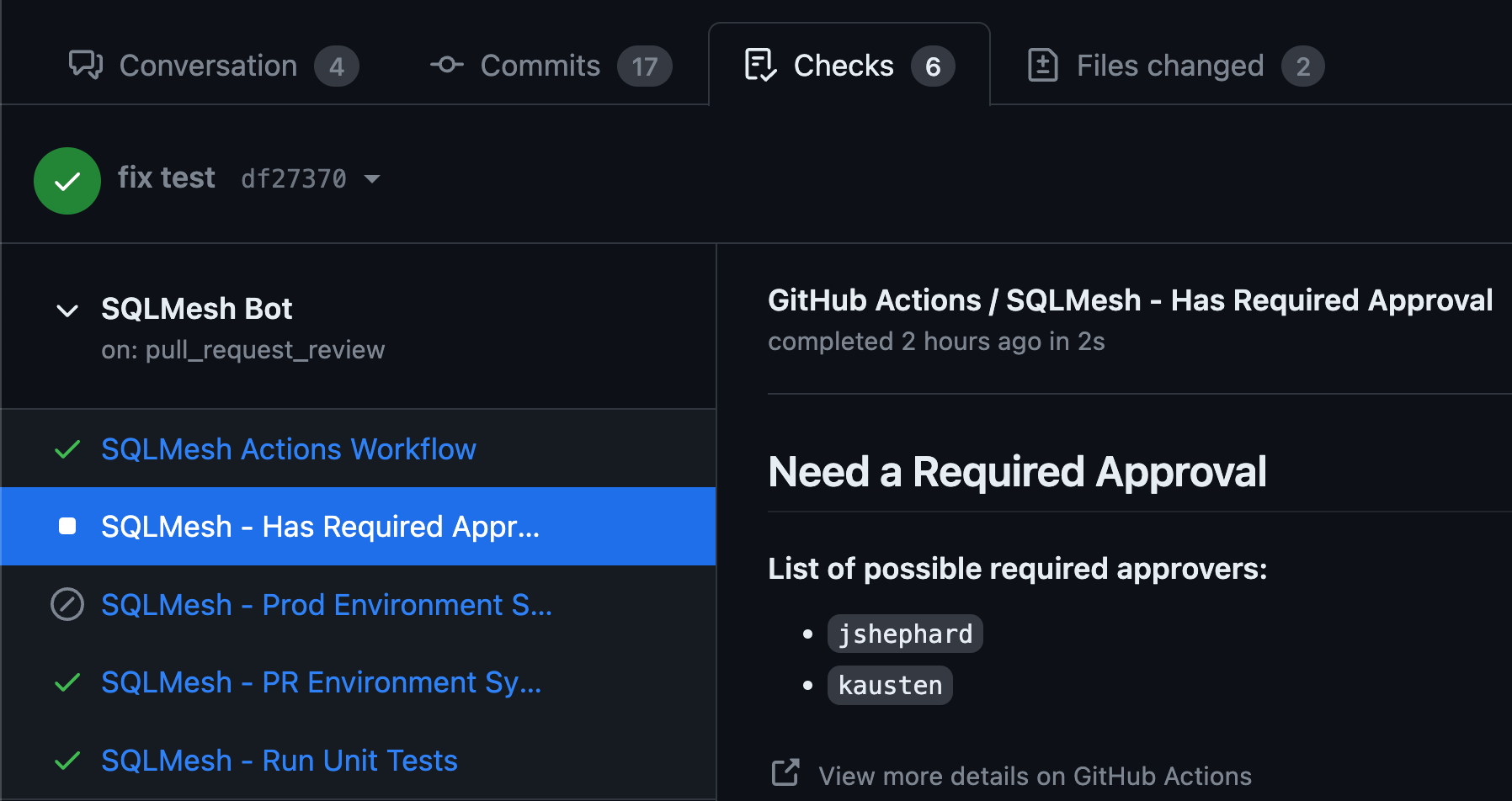
Enforce that certain reviewers have approved of the PR before it can be merged
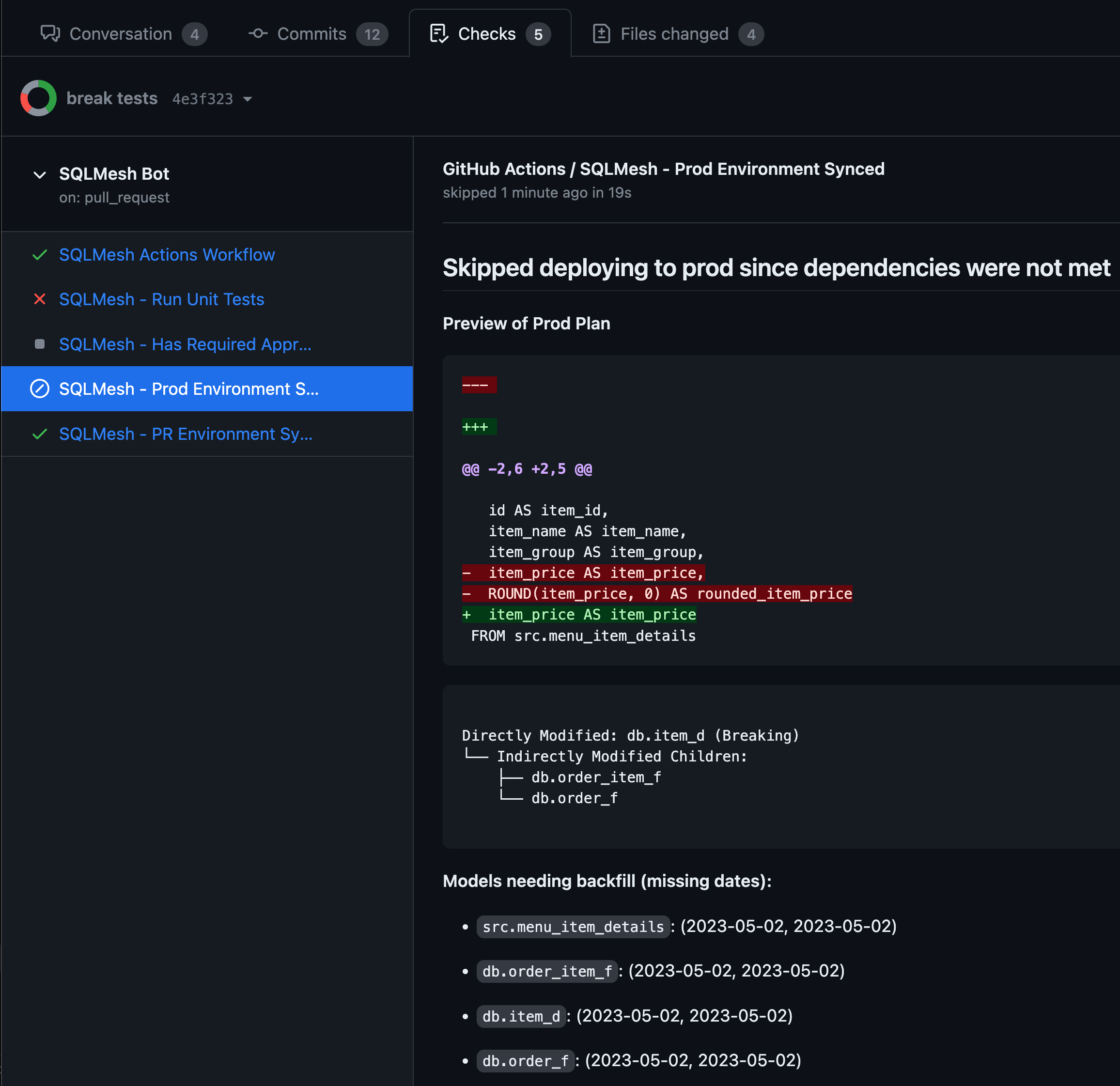
Preview Prod Plans before Deploying
Automatic deployments to production and merge